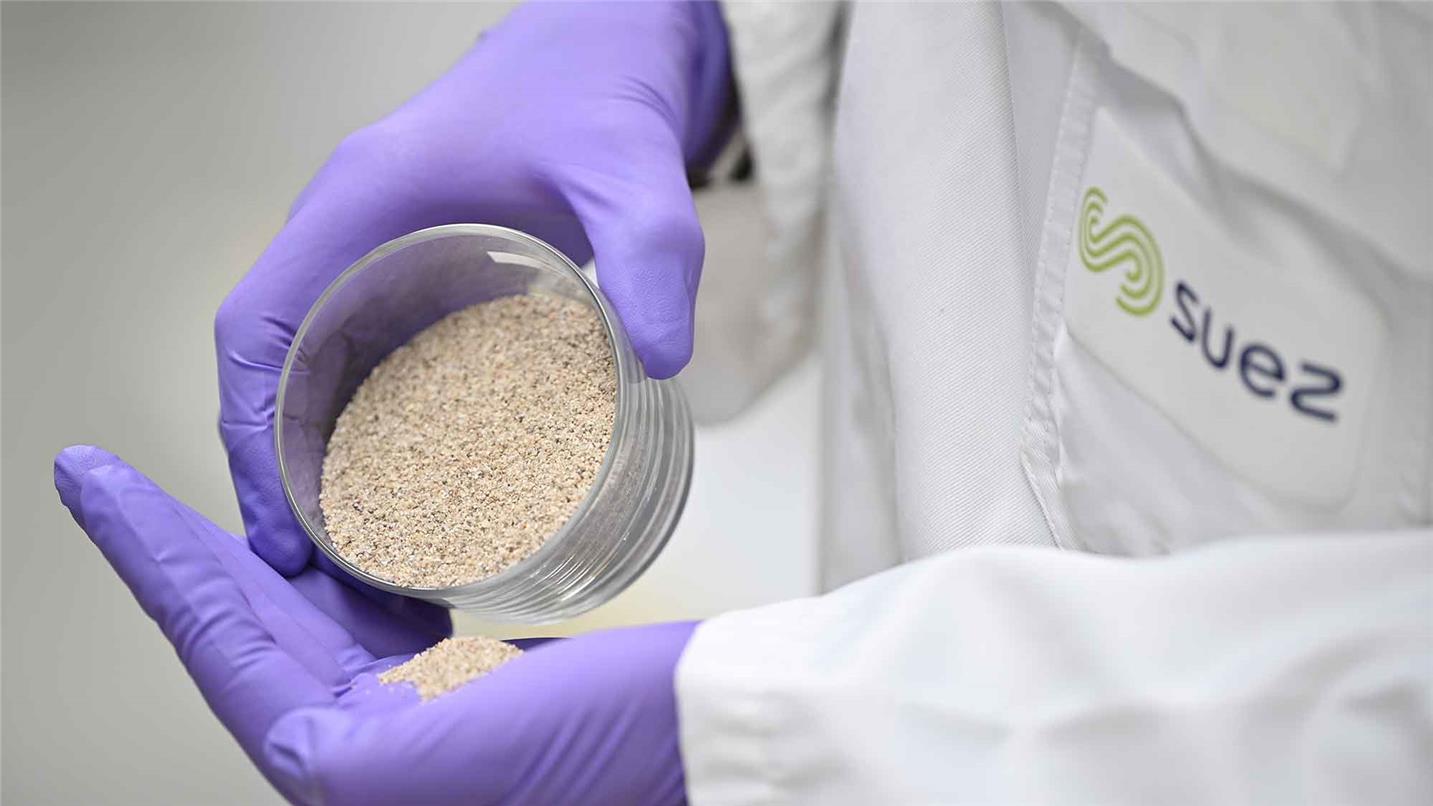
SUEZ innovation serving the essentials : water and waste
Credit: SUEZ group
We are innovating to address the challenges of today and tomorrow
Our established presence at the heart of our communities means that we are a trusted partner for our customers. Accordingly, our mission is to support them with the major ecological transitions and help them use resources more efficiently, more sustainably and more responsibly, and we are committed to working alongside them to:
Address the consequences of climate change
Preserve biodiversity
Reconcile development with social responsibility
Customer-centric innovation

In order to meet the growing needs of its customers and partners, SUEZ is currently increasing its capacity for innovationJérôme Bailly , Senior Vice President, Innovation, Research and Services
We use the passion and commitment of our teams to serve our customers, developing innovative solutions tailored to their needs.
To achieve these aims, we are focusing on innovation that is:

Targeted

User-oriented
Collaborative
Our priorities in terms of accelerating the major transitions
To help our customers manage water resources and waste more effectively, we are pursuing innovation projects focusing on 5 key themes.





Innovation at the heart of our strategy
To deal with the transformation of the environmental services sector and meet the increasing needs of our customers, we have been increasing our transformation, innovation and collaboration capabilities since 2022.
These greater resources will enable us to fulfil our new ambition, which embodied in our 2022-2027 strategy:
360° innovation
At SUEZ, we create resilient, innovative solutions that add a large amount of value in technical terms. We also innovate in order to create social value and encourage more sustainable consumption.
We take a 360° approach to innovation, allowing our customers to drive the ecological transition by relying on our strengths:
- Our historical expertise in engineering, construction and operations, which enables us to design facilities that are competitive and environmentally friendly and that create resources for communities.
- Our ability to offer performance-enhancing digital tools. At SUEZ, we use digital technology as a way of optimising the performance of our clients’ infrastructure, to increase waste sorting and recycling, and to preserve water quality. Day-to-day, our water and waste operational databases support the development of new solutions based on artificial intelligence.
- Our involvement in all parts of an innovation’s value chain and development cycle, from design to industrialisation, capitalising on the diversity of our sites and research centres.
- Our Open Innovation approach. Collaboration lies at the heart of our innovation approach. This is why we work closely with top universities and other academic institutions, and collaborate with large numbers of innovative startups and small and medium-sized companies.
- Supporting customers through behavioural, social and contractual innovation. We are building an integrated ecosystem so that we can have a complementary range of skills, in order to offer innovative financial models and help customers reduce their consumption of resources.
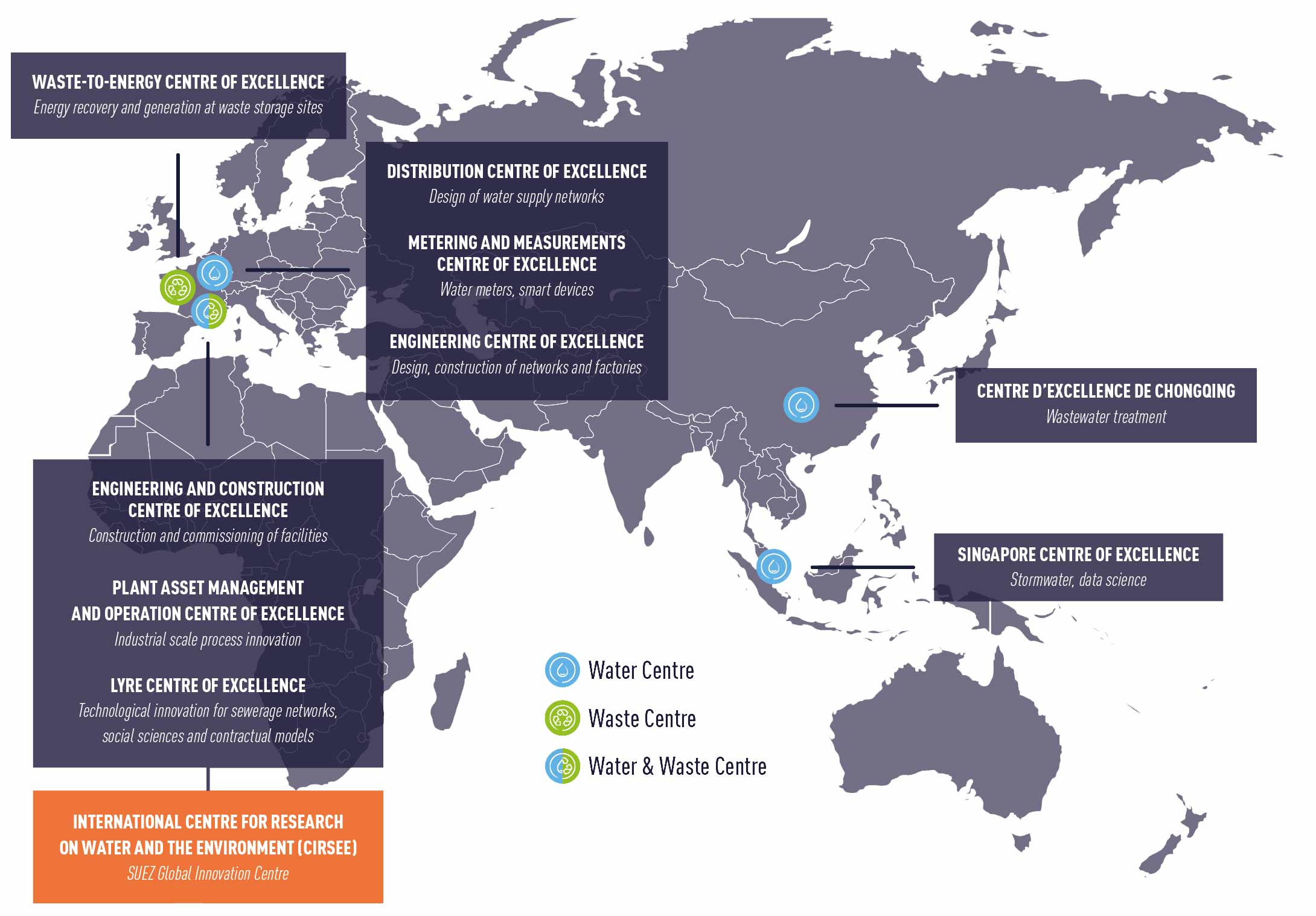
A network combining centres of excellence and experts working in the field
We are able to design and trial major innovations through our research centres of excellence around the world and our in-house network of over 1,300 experts across 20 countries, specialising in 19 areas covering water and waste but also broader topics such as healthcare, carbon and data.
Innovation Day 2025
SUEZ Innovation Day - 2025
Credit: SUEZ group

2025 Innovation Day Press Kit