One of our focus areas for SUEZ in India is to bring the Group’s expertise in waste recycling and recovery to India.
Scientific management of solid waste
In India, a major chunk of garbage remains untreated every single day. Metropolitan cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad, Bengaluru and Kolkata generate about 65 million tonnes of garbage every year and 80% of this waste is often disposed in unregulated dumps or openly burned. These practices have been creating serious health, safety, and environmental issues
In 2016, the Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) released a new Solid Waste Management Rules (SWM), 2016, which emphasized promotion of waste to energy plants, among others. The rules mandate all industrial units using fuel and located within 100 km from a solid waste-based Refuse-Derived Fuel (RDF) plant to make arrangements to replace at least 5 per cent of their fuel requirement by RDF so produced. The rules also direct that non-recyclable waste having calorific value of 1500 K/cal/kg or more shall be utilised for generating energy either through RDF, not disposed of on landfills and can only be utilised for generating energy either or through refuse derived fuel or by giving away as feed stock for preparing refuse derived fuel.
X
3
waste production in fast-growing urban areas is expected to nearly triple by 2025.
62
million tonnes of waste is generated annually in India
43
m
*Data as per the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
A complete range of Waste-to-Energy processes
Incineration
Anaerobic Digestion
Smart Cell
SRF* production plant
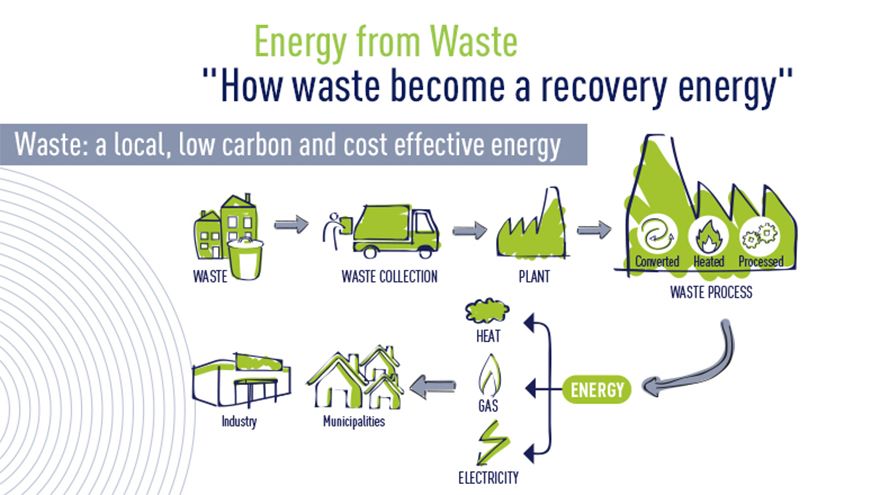
Recovering energy from our waste
Residual waste is any waste material that cannot be viably recycled. However, although this material cannot be recycled, it does represent an important source of energy. There are several processes that can be used to recover energy from residual waste, such as incineration in specialist energy from waste plants, methanation or the production of Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF) which converts the waste into solid fuel to replace coal used inenergy-intensive industries, such as cement works.
An Energy-from-waste plant transforms waste into electricity, heat or steam, which can be used to supply electricity grids and local heating networks or can be reintroduced into industrial processes. Energy recovery offers a competitive alternative to burying waste on storage sites (i.e. landfill), to fossil fuels and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.